Hardware Recommendations for Blender
We benchmark a wide range of hardware here at Puget Systems, and use the results to tailor systems for different workloads. Based on our testing, here is the hardware we recommend for Blender workstations.
Blender System Requirements and Benchmarks
Quickly Jump To: Processor (CPU) • Video Card (GPU) • Memory (RAM) • Storage (Drives)
Like most software developers, the Blender Foundation maintains a list of system requirements for Blender that can be used to help ensure the hardware in your computer system will work with their software. However, most “system requirements” lists tend to cover only the very basics of what hardware is needed to run the software, not what hardware will give the best performance. In addition, sometimes these lists can be outdated, show old hardware revisions, or simply contain sub-optimal hardware.
Because of how inconsistent these lists can be, here at Puget Systems we run benchmark tests on a wide range of hardware and publish our results to ensure that the systems we sell are perfectly tailored for your workload. Based on all our testing, here is our list of recommended hardware for a Blender PC.
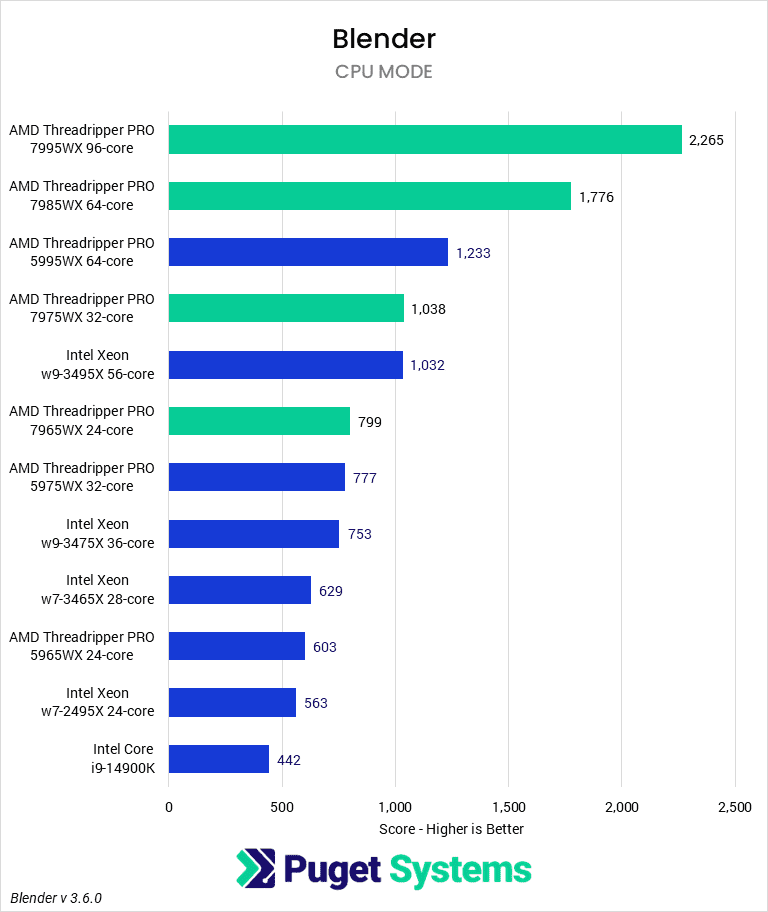
Processor (CPU)
How does Blender utilize the CPU?
The processor, or CPU, is one of the most important pieces of a Blender workstation. The CPU handles tasks such as modeling, animation, physics simulations, and rendering. While GPU rendering is significantly faster in Blender, the CPU can still provide increased performance.
What CPU is best for Blender?
Currently, the overall fastest CPU for Blender depends on your specific workflow. Modeling and animation tasks are better on a single, fast core. While rendering is better with large numbers of cores. Simulations are somewhat split. Cloth and rigid body simulations only use a few fast cores, while fluid simulations will use lots of cores.
If you will be doing a lot of fluid simulations, or relying on CPU rendering, then the current fastest CPU is AMD’s Threadripper™ 7995WX. It offers 96-cores, and support for up to a massive 1TB of RAM!
If you are focused on modeling and animation, then Intel’s Core™ Ultra and AMD’s Ryzen™ 9000 Series processors are the best option. Lower core count models like the Core Ultra 7 265K and Ryzen 7 9700X are more affordable, while higher core count versions like the Ultra 9 285K and Ryzen 9 9950X will offer better CPU-based rendering if needed.
Does CPU clock speed improve Blender workflows?
High clock speeds have the greatest impact on modeling and animation, especially as projects become more complex.
Do more CPU cores make Blender faster?
More cores will speed up some actions such as rendering and fluid simulations, so if those tasks take up a lot of your time then maxing out the number of cores you can afford would be ideal. Additional cores will not speed up modeling and animation, though, as those are single- or lightly-threaded.
Does Blender work better with Intel or AMD CPUs?
At the moment, AMD has a lead in rendering and other well-threaded workloads due to their high CPU core counts. However, Intel’s processors tend to offer higher per-core clock speeds – making them better for modeling tasks.
Can I use a laptop for Blender?
Yes, though even top-end mobile CPUs and GPUs will be a little slower than similar desktop hardware. Our new mobile workstation is ideal for this application, and you can read about trade-offs with a traditional tower PC in our comparison article.
Recent Blender CPU Articles:
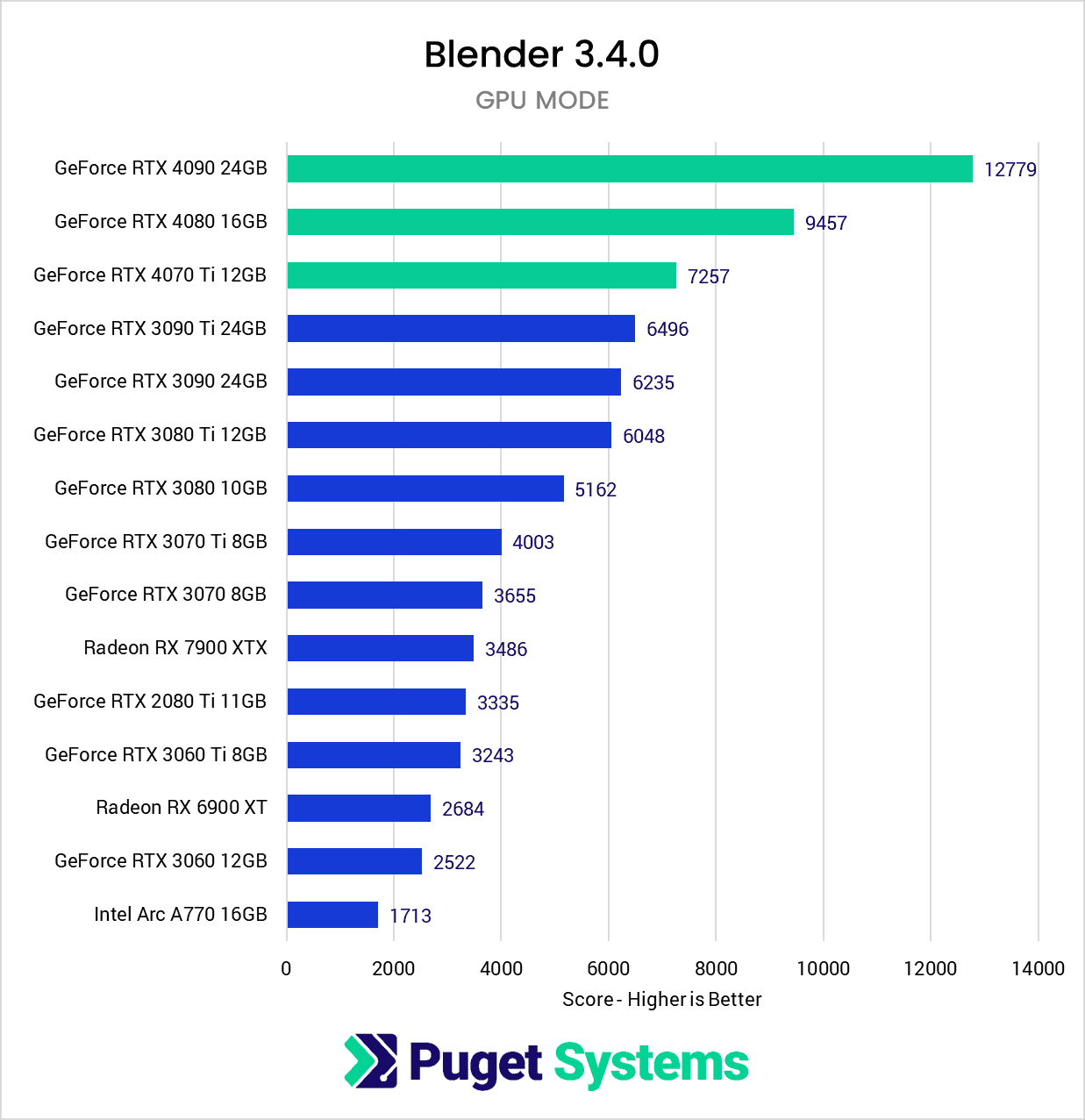
Video Card (GPU)
How does Blender utilize video cards (GPUs)?
The video card, or GPU, is responsible for how many models, textures, and effects can be displayed on the screen as well as how many frames per second can be displayed. Blender also utilizes the GPU for its built-in rendering engine.
What GPU (video card) is best for Blender?
Currently, the fastest GPU for Blender is the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090. The other RTX 40 & 50 Series cards also perform quite well, though!
How much VRAM (video memory) does Blender need?
The amount of VRAM needed will depend on the complexity of the project and the final resolution. Running out of VRAM results in a significant performance decrease as it will need to use system memory to make up the difference, so it is safest to err on the high side and get a video card with more onboard memory than you need if you are unsure. This article from CGDirector may also help.
Will multiple GPUs improve performance in Blender?
Only one video card is used for displaying content on-screen in Blender, but the built-in rendering engine is able to utilize multiple GPUs while rendering.
Does Blender work better with NVIDIA or AMD graphics cards?
NVIDIA cards have a significant performance lead over AMD when it comes to rendering due to the OptiX and CUDA APIs.
Does Blender need a professional video card, like a Quadro?
There is no specific need for a professional grade GPU, but it is worth noting that such cards often come equipped with more onboard memory (VRAM) than consumer class GPUs. If your workload needs a particularly high amount of VRAM, then it may be worth considering a pro card.
Recent Blender GPU Articles:
Memory (RAM)
RAM is used to store any running applications, as well as any simulation or rendering caches. If a system needs more RAM than is available, it begins using the hard drive to store and read this information. A hard drive is much slower at this than RAM is, and results in slower load times and frame rates.
How much RAM does Blender need?
The amount of RAM needed depends on the specific workflow. Blender itself can function in a system with 16GB of RAM, as long as the projects are small. Larger projects will require 32GB. Another factor to consider is what other apps are being used alongside Blender. Many artists will have several high-end applications open at the same time and would need 64GB of RAM or more. In our experience, 64 to 128GB is generally the range for most high-end users.
Storage (Drives)
Storage needs for Blender are often overlooked. Blender projects can range from small to very large as scene complexity increases. Those that are rendering high-resolution animations will also need large and fast storage. Many users also have large libraries of projects or reference files, so it is important to get the right drive for the task.
What storage configuration works best for Blender?
Having both large and fast storage is highly advisable. We recommend having one 500GB+ NVMe solid-state drive for the OS and applications, and another 1 or 2TB NVMe SSD for your project files. This should be enough for most users, but many artists will also want another large drive for their material and reference libraries. This can be a slower SATA SSD or even platter drive, depending on your budget and capacity needs. If you want additional mass storage, backup, or archival, an internal or external hard drive works well for that and is less expensive than a high capacity SSD.
Should I use network attached storage for Blender?
Network-attached storage is another consideration. It’s become more common for workstation motherboards to have 10Gb Ethernet ports, allowing for network storage connections with reasonably good performance without the need for more specialized networking add-ons.