Table of Contents
Update: Our initial version of this article included some incorrect values for the NVIDIA RTX 4070. The charts have now been updated to correct the results and bring the 4070 in line with the rest of the NVIDIA cards.
Introduction
Topaz Video AI is a popular software package that utilizes AI to enhance video for a variety of reasons, most commonly for upscaling and frame interpolation (slow motion). Like many AI solutions, your choice of GPU makes a significant impact on how fast the software performs. Because of that, it is critical to know just how different GPUs perform across the various brands and models that are available, so that you can make sure you are getting the highest possible performance for your dollar.
In past articles, our testing was done by semi-manually applying different settings to a project and measuring the performance. However, since then, Topaz Labs has included a built-in benchmark function in order to quickly and easily measure the performance for a range of tasks in Topaz Video AI. The benchmark still needs to be launched via the GUI (although we are encouraging Topaz Labs to make it runnable via the command line), but it is significantly easier to run and keep updated than our previous methods.
With this benchmark functionality now available, we decided it was a good time to examine how various modern (and older) consumer GPUs, including NVIDIA GeForce, AMD Radeon, and Intel Arc, perform in Topaz Video AI.
Test Setup
Test Platform
| CPU: AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 7975WX |
| CPU Cooler: Asetek 836S-M1A 360mm |
| Motherboard: ASUS Pro WS WRX90E-SAGE SE BIOS version: 0404 |
| RAM: 8x DDR5-5600 16 GB (128 GB total) Running at 5200 Mbps |
| PSU: Super Flower LEADEX Platinum 1600W |
| Storage: Samsung 980 Pro 2TB |
| OS: Windows 11 Pro 64-bit (22631) |
Benchmark Software
| Topaz Video AI 5.1.3 |
Tested GPUs
To test how Topaz Video AI performs with different GPUs, we built up a standard testbed intended to minimize the potential for bottlenecks in the system outside of the GPU. We are using the 32-core AMD Ryzen Threadripper PRO 7975WX and 128 GB of DDR5 memory, which should give us the best overall performance. For each GPU, we are using the latest available driver version as of July 1st, 2024 (sticking with the “Studio” drivers for NVIDIA), and ran the built-in benchmark at both 1920×1080 and 3840×2160 resolutions.
The one thing the Topaz Video AI benchmark lacks is any sort of scoring system. It provides FPS results for 20 different tests, but it can be hard to draw general conclusions from such a large number of results. Because of this, we came up with our own scoring system, based on the same methodology used in our PugetBench suite of benchmarks:
Enhancement Score = geomean(Artemis 1X, Artemis 2X, ...) * 10
SlowMo Score = geomean(4X Slowmo Apollo, 4X Slowmo APFast, ...) * 10
Overall Score = geomean(Enhancement Score, SlowMo Score) * 10This scoring combines all the “Enhancement” tests (Artemis _X, Iris _X, Proteus _X, Gaia _X, Nyx _X) and “Slowmo” tests across both 1920×1080 and 3840×2160 resolutions using a geometric mean. We then multiply that by 10 to keep the numbers within the typical range for this type of benchmark.
From those two scores, we combine them (again using a geometric mean) and multiply by 10 again to get an “Overall Score.” We often like to make these Overall Score bigger to differentiate them from the scores from which they are calculated, hence multiplying the result by 10.
We separated the Enhancement and Slowmo tests because, from our results, this appears to be a relatively consistent way to examine performance across different GPU brands and families. Some of the individual tests show more nuanced differences (which is why we provide all the raw results if you only care about one aspect of Topaz Video AI), but we found that you can get most of the valuable information needed to decide which GPU fits your needs with these three scores.
Raw Benchmark Results
While we will discuss our testing in detail in the next sections, we often provide the raw results for those who want to dig into the details. If you tend to perform a specific codec or task in your workflow, examining the raw results will be much more applicable than our more general analysis.
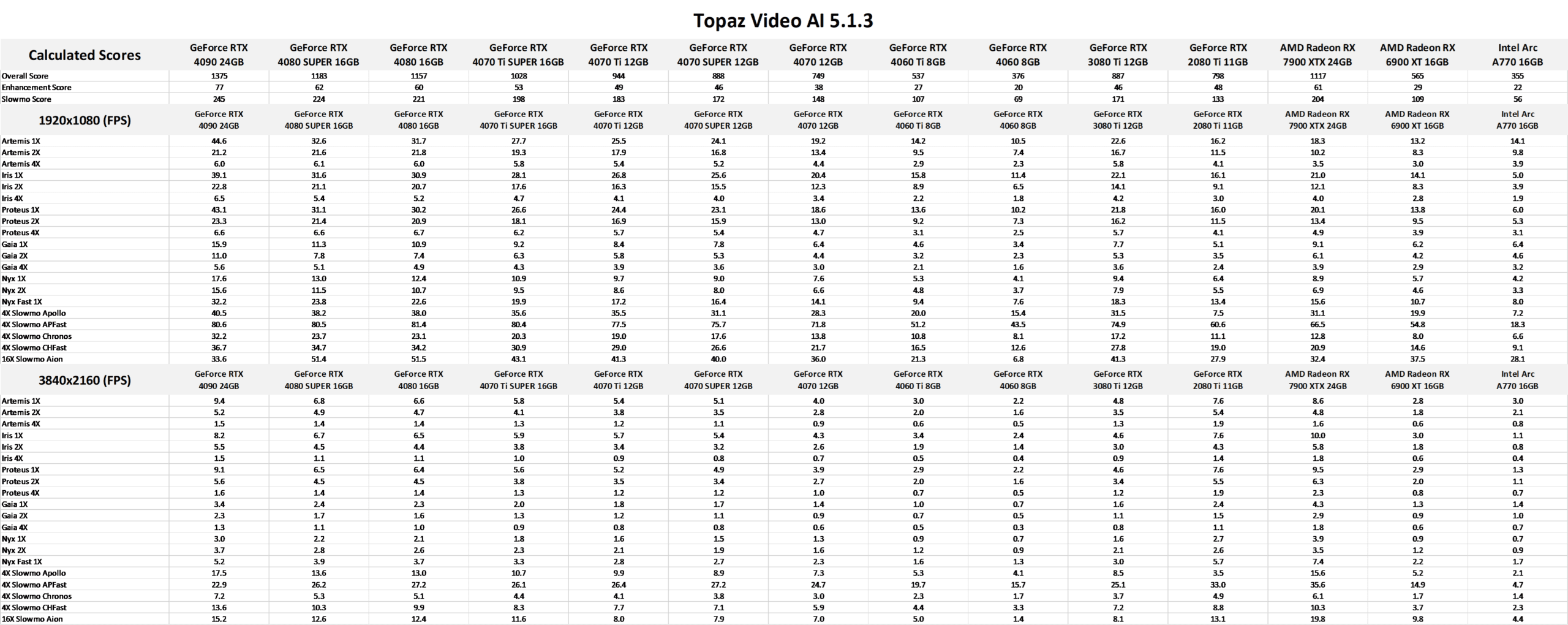
Overall GPU Performance
Before we get into the results, we want to note that since we are testing 14 different GPUs, our charts are quite a bit taller than normal. We apologize to anyone on mobile or a smaller screen! Also, since we are not focusing on any GPU in particular, we colored the top GPU models from NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel in green to help make it obvious how each brand stands in terms of maximum performance.
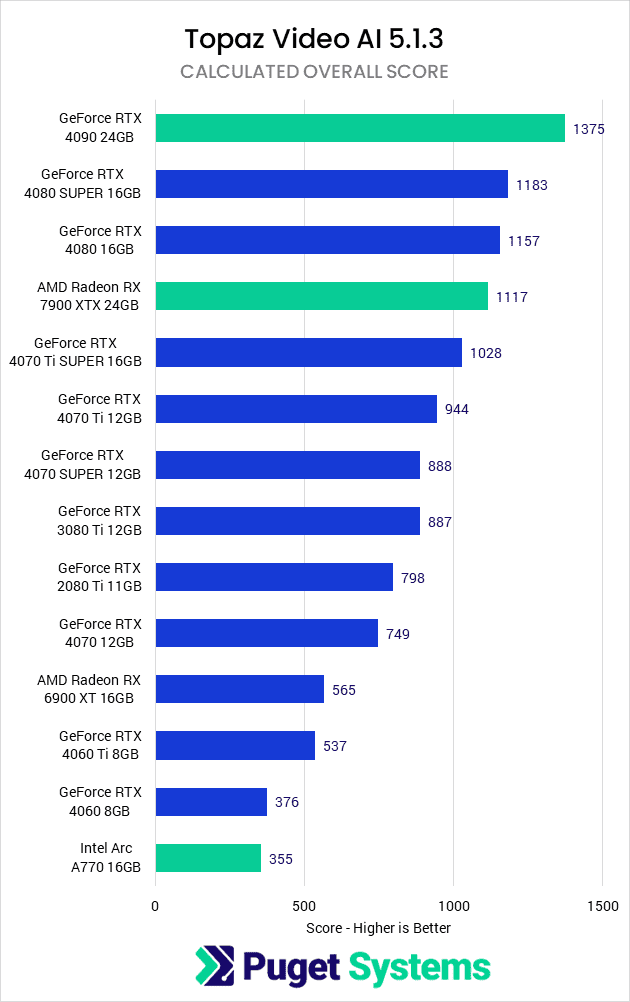
Starting off, we are going to take a look at the Overall Score that we calculated based on all the results from the Topaz Video AI built-in benchmark running at both 1920×1080 and 3840×2160. This score factors in the results for all the tests, and should be a good indicator of how different GPUs compare for general use in Video AI.
There is a LOT of data in here, but there are a handful of primary questions we can answer directly. The first is AMD vs. Intel vs. NVIDIA GPU performance, and it is clear that NVIDIA GeForce gives the highest overall performance with the RTX 4090 topping the chart. AMD doesn’t have as high-end (or as expensive) of a GPU as NVIDIA’s RTX 4090, but at a similar price point (Radeon 7900 XTX 24GB vs. GeForce RTX 4080 SUPER 16GB), AMD is only 6% behind. In terms of pure performance, NVIDIA is the way to go, but the additional VRAM that tends to be found on AMD GPUs could make a difference depending on your workflow.
The Intel Arc A770 result may look bad, but it is worth keeping in mind that it is also one of the least expensive GPUs we tested. The A770 has an MSRP of $329, compared to the RTX 4060 MSRP of $299. That is a $30 difference, but similar to what we just discussed with AMD, the Intel Arc A770 has a lot more VRAM than the RTX 4060 (16GB vs 8GB). So, while it is at the bottom of this chart, that doesn’t actually mean it is necessarily a poor choice for those on a tight budget as it is only 6% slower than the RTX 4060.
The last thing we want to point out from these results is just how much using a newer-generation GPU can impact performance. For example, the Radeon 7900 XTX is almost exactly two times faster than a Radeon 6900 XT, and the RTX 4080 SUPER is 35% faster than the RTX 3080 Ti or 50% faster than the older RTX 2080 Ti.
Enhancement GPU Performance

Going one step deeper than the Overall Score, we are looking at performance for the “Enhancement” portion of the benchmark, which includes tests using the Artemis, Iris, Proteus, Gaia, and Nyx AI models.
For these tests, Intel does a bit better, with the Arc A770 moving up to be slightly faster than the RTX 4060. AMD also slightly improves compared to NVIDIA, with the Radeon 7900 XTX 24GB now performing within the margin of error of the RTX 4080 SUPER 16GB. This makes the 7900 XTX the overall better choice in terms of performance and VRAM capacity at this price point due to its higher VRAM.
Other than those two minor differences, the results are very similar to the Overall Score in the previous section.
Slowmo GPU Performance
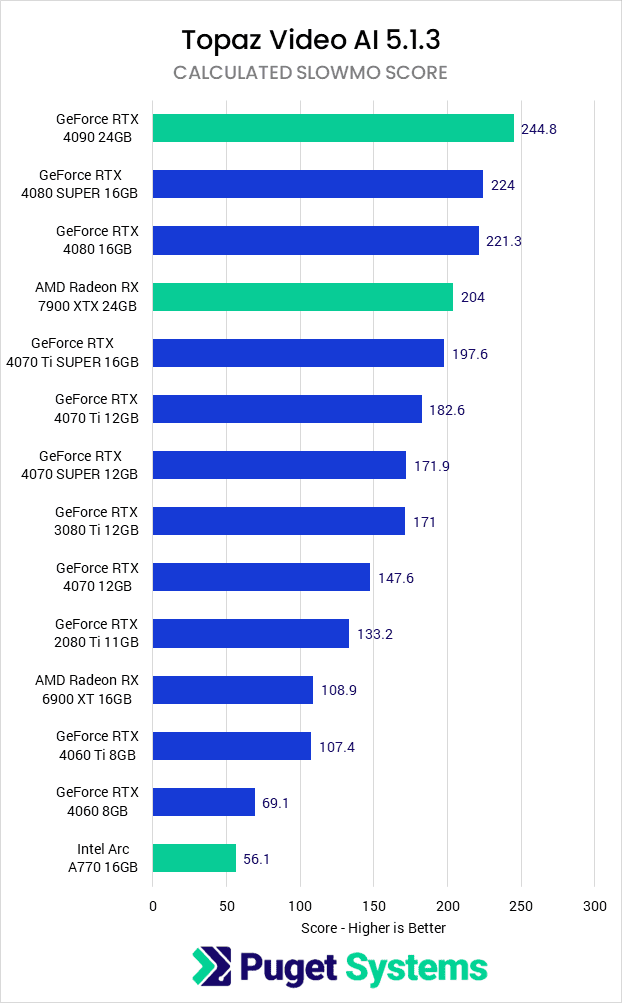
Last up, we have the calculated score for Slowmo, which includes the Apollo, APFast, Chronos, CHFast, and Aion AI models. Given that this score is the other half of what makes up the Overall Score, the main points of discussion here are basically the opposite of the previous section.
For these tests, both Intel and AMD take a bit of a hit to performance relative to NVIDIA. The Intel Arc A770 drops to the bottom of the chart, coming in at about 80% of the performance of the RTX 4060. The AMD Radeon 7900 XTX also drops, ending up slightly slower than the NVIDIA RTX 4070, or about 90% of the performance of the similarly priced RTX 4080 SUPER.
What is the Best Consumer GPU for Topaz Video AI 5.1?
Topaz Video AI is unique in that there are a large number of terrific GPU options. For AI solutions like this, NVIDIA tends to be the best choice for performance, but while that holds true at the top end with the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 topping our performance charts, both AMD and Intel are solid in terms of performance-per-dollar.
For example, AMD’s Radeon 7900 XTX 24GB was only about 5% slower than the similarly priced NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4080 SUPER 16GB. That is a fairly small difference in performance (although it can add up if you process a lot of videos), and some workflows may value the 24GB of VRAM on the 7900 XTX over the small drop in performance.
Intel is a very similar story, just at a lower price point. The Intel Arc A770 16GB has an MSRP of $329, which puts it about in line with the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 8GB ($299 MSRP). Again, the difference in performance is only about 5%, but the A770 has twice the VRAM (16GB vs 8GB). 8GB is likely enough VRAM for people working at this budget level, but it can be very nice to have more VRAM than you need just for peace of mind.
In general, we lean towards NVIDIA GPUs as they tend to give the highest performance and reliability across various content creation workflows, but if performance in Topaz Video AI is your primary concern, it is great to see that there are almost no bad choices. The single biggest recommendation we have is to make sure you are getting the latest generation GPU from each brand, as newer cards do give a good uplift to performance over previous generation models. Beyond that, almost any NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel GPU appears to give great performance, giving you the freedom to choose whichever brand of GPU you prefer that fits within your budget.
If you need a powerful workstation for content creation, the Puget Systems workstations on our solutions page are tailored to excel in various software packages. If you prefer to take a more hands-on approach, our custom configuration page helps you to configure a workstation that matches your exact needs. Otherwise, if you would like more guidance in configuring a workstation that aligns with your unique workflow, our knowledgeable technology consultants are here to lend their expertise.


