Table of Contents
Introduction
The latest generation from NVIDIA, the RTX 40 Series, follows the company’s tradition of staggered launches with the separate release of the RTX 4090, 4080, and now, the RTX 4070 Ti 12GB. After the debut of the GeForce RTX 4080 16GB in November and the GeForce RTX 4090 24GB in October, the top three GPUs of the series are now available. At Puget Systems, we believe it’s the ideal moment to perform comprehensive testing on the performance of these 40 series cards in various content creation tasks, including 3D rendering and video editing. Our focus in particular, will be on Redshift from Maxon.

In this article, we will use the benchmark built into Redshift from Maxon to examine the GeForce RTX 40 Series performance for GPU rendering. As a comparison, we will include the full lineup from the previous generation GeForce RTX 30 Series, and the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti for additional context. Currently, Redshift only supports NVIDIA GPUs in Windows, so there isn’t a competing product from AMD or Intel for us to compare to.
If you want to read more about the new GeForce RTX 40 Series cards (including the 4070 Ti, 4080, and 4090) and what sets them apart from the previous generation, we recommend checking out our main NVIDIA GeForce 40 Series vs AMD Radeon 7000 for Content Creation article. That post includes more detailed information on the GPU specifications, testing results for various other applications, and the complete test setup details for the hardware and software used in our testing.
Overall Redshift Performance Analysis
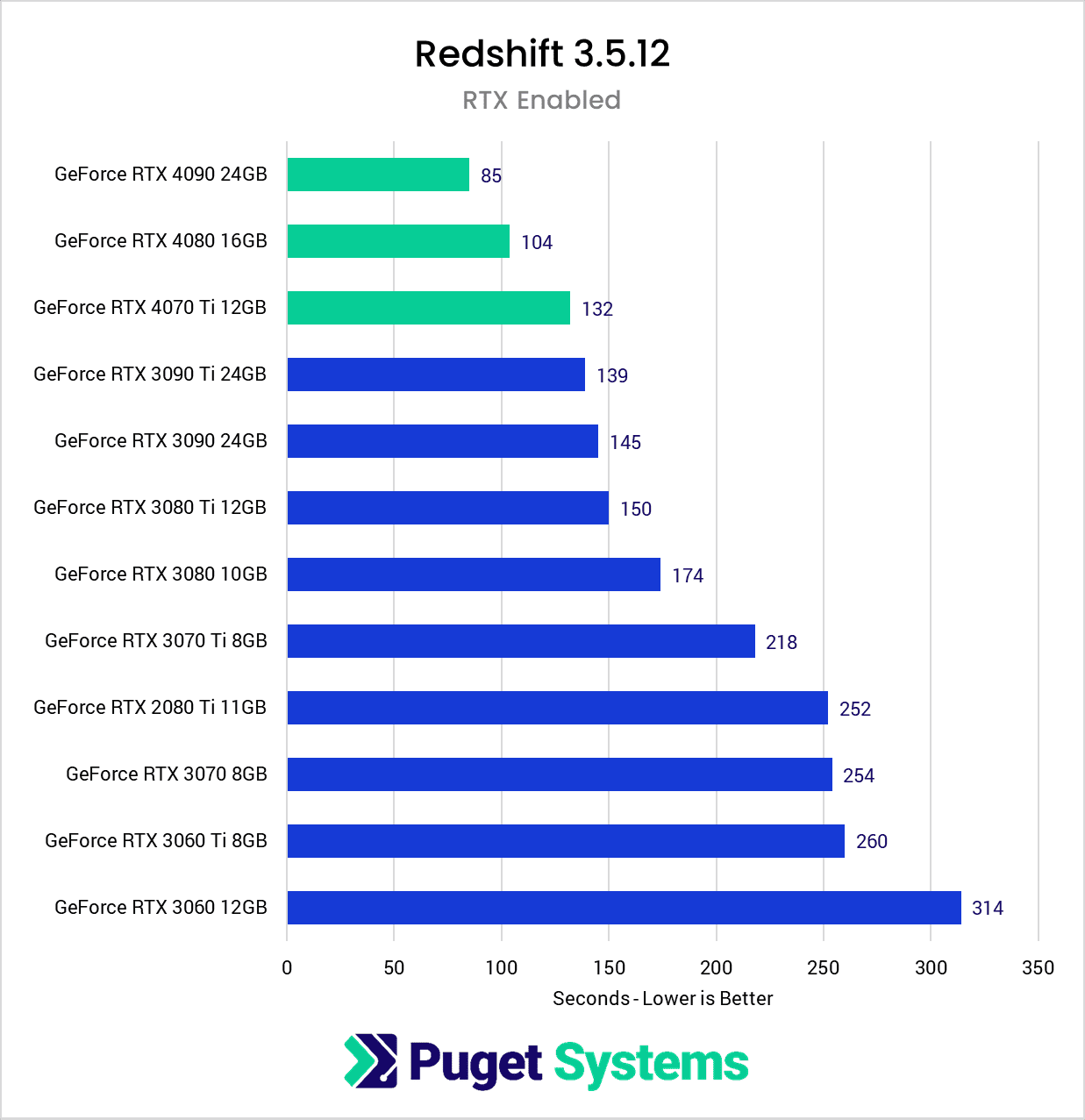
As we can see, the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series GPUs are currently the fastest GPUs available for rendering in Redshift. The newest release, the RTX 4070 Ti 12GB, is faster than even the fastest GPU from the previous generation RTX 30 Series. At a quick glance, all three of these video cards will be great options for GPU rendering. Next, we’ll dig into these results to get a more detailed look at how these stack up.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series vs RTX 30 Series
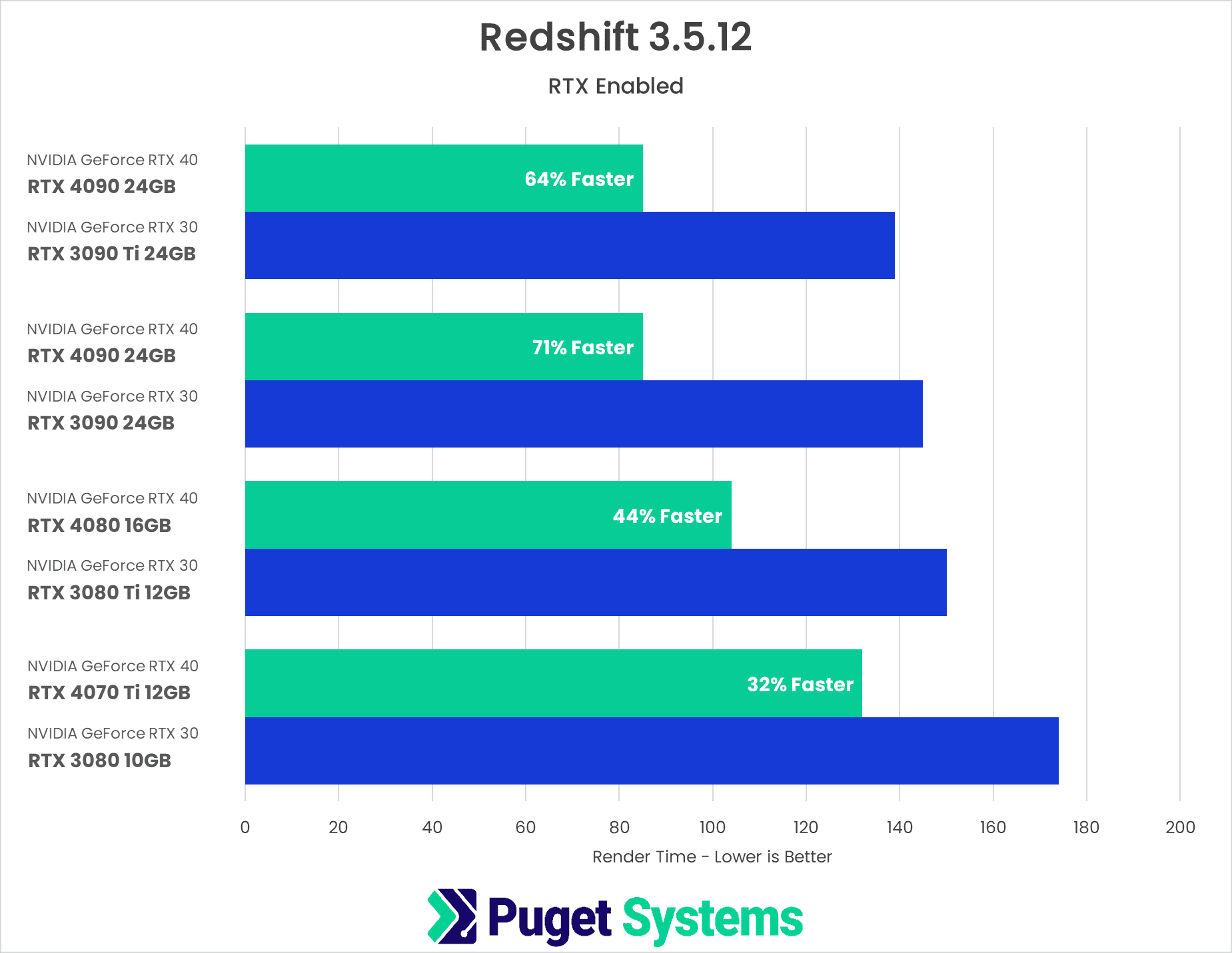
In the above chart, we compare the new generating of cards versus their closest price equivalent in the previous generation. Due to changes in architecture, supply chain, and the like, NVIDIA is not always consistent with its naming scheme, so this gives a better comparison of what performance to expect at a given price point. We added the top-of-the-line RTX 3090 Ti just because it doesn’t have a price equivalent at this point.
Starting with the RTX 4090 24GB, it is 71% faster at completing the render than the RTX 3090 for only a 7% price increase. This isn’t as large of an improvement as we see in other GPU rendering engines, but this is likely a limitation of the benchmark itself as opposed to the GPU’s potential. The RTX 4090 also outpaces the much more expensive RTX 3090 Ti, a GPU less than a year old. For those looking for the best-performing GPU for rendering, the RTX 4090 24GB is hands down the best option.
Moving on to the RTX 4080 16GB, this GPU costs the same as the RTX 3080 Ti yet delivers 44% faster renders. It also increases the available VRAM from 12GB to 16GB, allowing for larger and more complex renders, something most users will appreciate. Again, this is an excellent gen-over-gen improvement.
Lastly, we look at the latest release, the RTX 4070 Ti 12GB. This GPU is $100 more than the RTX 3080 10GB (roughly 14% more expensive). It returns 32% faster rendering performance for that extra cost and brings an additional 2GB of VRAM. While this is still a welcome upgrade over the RTX 3080, it’s not nearly as impressive as the RTX 4090 and 4080. If we compare by product name, the new RTX 4070 Ti is 61% faster than the RTX 3070 Ti but also 33% more expensive. However we compare it, the RTX 4070 Ti provides more performance than the cost increase but is overshadowed by its more powerful siblings.
NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series vs GeForce RTX 20 Series
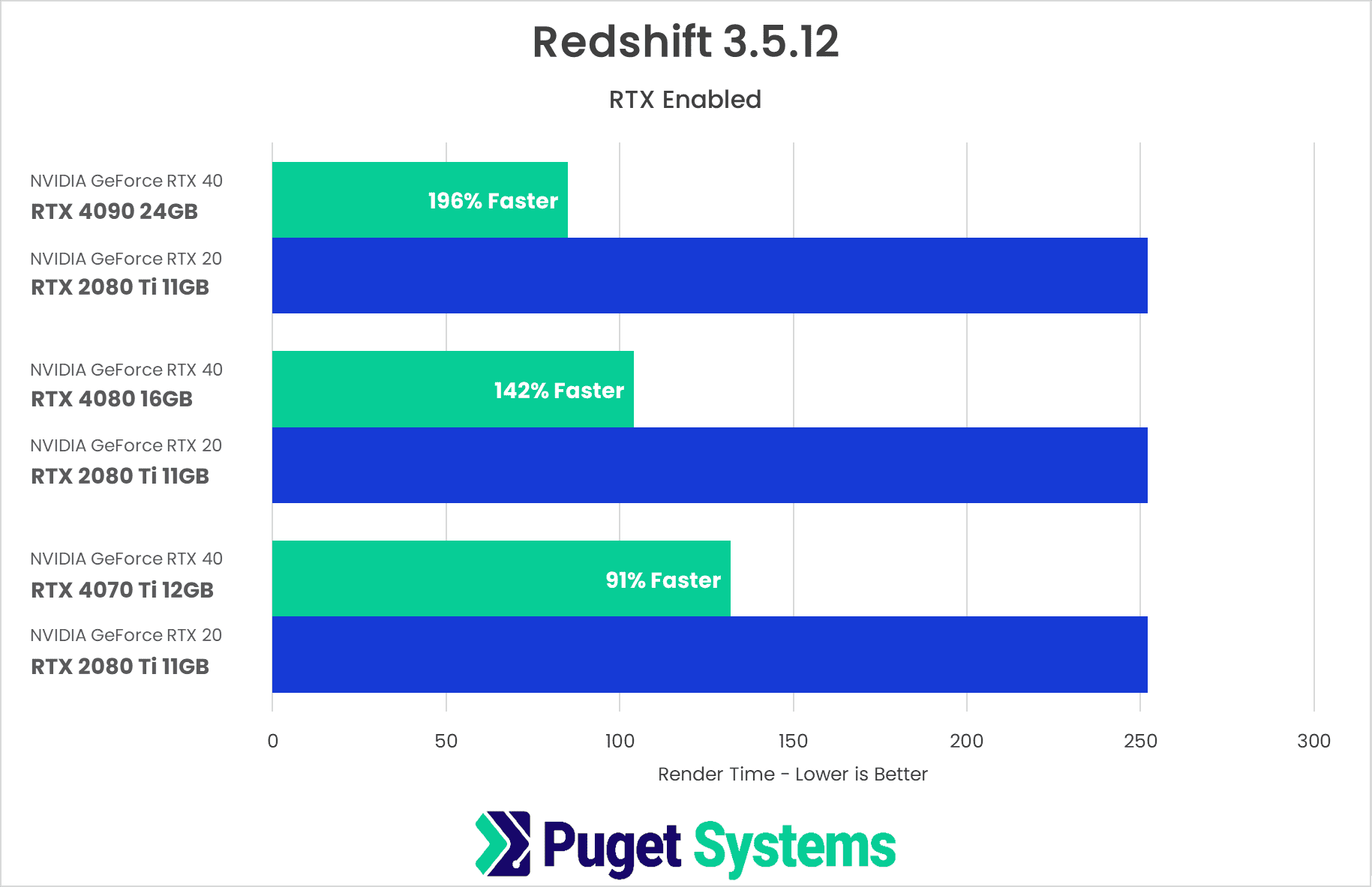
Most users don’t upgrade every generation, so we thought we’d take a moment to compare the new GPUs to the rendering king from only a few years ago. This is less of a price comparison and more just to show how much improvement a user could expect if they think it is time to upgrade. As the chart shows, if someone were to upgrade from a 2080 Ti, they would see improvements anywhere from 2x to 3x faster renders. This sort of speed increase could likely be applied to Cinema4D’s new simulation systems as well, making for a great all-around improvement.
How Well Do the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series Perform in Redshift?
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 40 Series brings considerable improvements in Redshift GPU rendering performance compared to the RTX 30 Series. The top performer, the RTX 4090 24GB, is 71% faster in Redshift compared to the previous generation’s RTX 3090. The RTX 4080 16GB has a smaller, but still welcomed 44% improvement in speed when compared to the similarly priced RTX 3080 Ti. Although not as impressive as the RTX 4080 or RTX 4090, the RTX 4070 Ti 12GB also delivers a large 32% faster rendering performance compared to the RTX 3080, although it is 14% more expensive. This increased performance is enough that it enables the 4070 Ti to outperform the RTX 3090 Ti, a video card that is only a year old and costs twice as much.
It is worth noting that these tests do not consider the amount of VRAM available. With GPU rendering, VRAM can become constrained somewhat easily as scenes become larger and more detailed. This can lead to “out of memory” errors or defaulting back to CPU rendering and losing out on GPUs’ speed advantages. Also, note that NVLink is not offered on any of these GPUs, so pooling the VRAM of two GPUs is no longer an option.
Keep in mind that the benchmark results in this article are strictly for Unreal Engine and that performance will vary widely in different applications. If your workflow includes other software packages, we highly recommend checking out our NVIDIA GeForce 40-Series vs AMD Radeon 7000 for Content Creation article, which includes results and links to in-depth testing for a range of other applications, including Premiere Pro, After Effects, DaVinci Resolve, Unreal Engine, and Blender.


